spring 就像一把瑞士军刀, 由诸多实用的零部件组成, 按需使用, 自由分配, 于之我们开发人员来说, 无疑是把利器, 但在使用时, 不仅仅是只能简单使用, 更要了解 它的实现原理, 以及向上增加其他的实用零部件, 本篇文章简单记录一下 DispatchServlet 的处理逻辑, 以及顺带的几个重要节点编程技巧, 仔细阅读可为你在 mvc 编程中 带来一些意想不到的实用技巧
DispatchServlet DOC
看这个类之前需要先看一下它的 doc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
/**
* Central dispatcher for HTTP request handlers/controllers, e.g. for web UI controllers
* or HTTP-based remote service exporters. Dispatches to registered handlers for processing
* a web request, providing convenient mapping and exception handling facilities.
*
* <p>This servlet is very flexible: It can be used with just about any workflow, with the
* installation of the appropriate adapter classes. It offers the following functionality
* that distinguishes it from other request-driven web MVC frameworks:
*
* <ul>
* <li>It is based around a JavaBeans configuration mechanism.
*
* <li>It can use any {@link HandlerMapping} implementation - pre-built or provided as part
* of an application - to control the routing of requests to handler objects. Default is
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping} and
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping}.
* HandlerMapping objects can be defined as beans in the servlet's application context,
* implementing the HandlerMapping interface, overriding the default HandlerMapping if
* present. HandlerMappings can be given any bean name (they are tested by type).
*
* <li>It can use any {@link HandlerAdapter}; this allows for using any handler interface.
* Default adapters are {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter},
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter}, for Spring's
* {@link org.springframework.web.HttpRequestHandler} and
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller} interfaces, respectively. A default
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter}
* will be registered as well. HandlerAdapter objects can be added as beans in the
* application context, overriding the default HandlerAdapters. Like HandlerMappings,
* HandlerAdapters can be given any bean name (they are tested by type).
*
* <li>The dispatcher's exception resolution strategy can be specified via a
* {@link HandlerExceptionResolver}, for example mapping certain exceptions to error pages.
* Default are
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver},
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver}, and
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver}.
* These HandlerExceptionResolvers can be overridden through the application context.
* HandlerExceptionResolver can be given any bean name (they are tested by type).
*
* <li>Its view resolution strategy can be specified via a {@link ViewResolver}
* implementation, resolving symbolic view names into View objects. Default is
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver}.
* ViewResolver objects can be added as beans in the application context, overriding the
* default ViewResolver. ViewResolvers can be given any bean name (they are tested by type).
*
* <li>If a {@link View} or view name is not supplied by the user, then the configured
* {@link RequestToViewNameTranslator} will translate the current request into a view name.
* The corresponding bean name is "viewNameTranslator"; the default is
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator}.
*
* <li>The dispatcher's strategy for resolving multipart requests is determined by a
* {@link org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartResolver} implementation.
* Implementations for Apache Commons FileUpload and Servlet 3 are included; the typical
* choice is {@link org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver}.
* The MultipartResolver bean name is "multipartResolver"; default is none.
*
* <li>Its locale resolution strategy is determined by a {@link LocaleResolver}.
* Out-of-the-box implementations work via HTTP accept header, cookie, or session.
* The LocaleResolver bean name is "localeResolver"; default is
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver}.
*
* <li>Its theme resolution strategy is determined by a {@link ThemeResolver}.
* Implementations for a fixed theme and for cookie and session storage are included.
* The ThemeResolver bean name is "themeResolver"; default is
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver}.
* </ul>
*
* <p><b>NOTE: The {@code @RequestMapping} annotation will only be processed if a
* corresponding {@code HandlerMapping} (for type-level annotations) and/or
* {@code HandlerAdapter} (for method-level annotations) is present in the dispatcher.</b>
* This is the case by default. However, if you are defining custom {@code HandlerMappings}
* or {@code HandlerAdapters}, then you need to make sure that a corresponding custom
* {@code RequestMappingHandlerMapping} and/or {@code RequestMappingHandlerAdapter}
* is defined as well - provided that you intend to use {@code @RequestMapping}.
*
* <p><b>A web application can define any number of DispatcherServlets.</b>
* Each servlet will operate in its own namespace, loading its own application context
* with mappings, handlers, etc. Only the root application context as loaded by
* {@link org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener}, if any, will be shared.
*
* <p>As of Spring 3.1, {@code DispatcherServlet} may now be injected with a web
* application context, rather than creating its own internally. This is useful in Servlet
* 3.0+ environments, which support programmatic registration of servlet instances.
* See the {@link #DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext)} javadoc for details.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rob Harrop
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @author Sebastien Deleuze
* @see org.springframework.web.HttpRequestHandler
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller
* @see org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
*/
DispatchServlet 如何初始化
这个类实例化, 有两种方法
1. 继承 AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer, spring 为了容器单独设计了 SpringServletContainerInitializer, 如果使用外部容器(非嵌入式)的情况下, 容器启动后, 通过 SPI 加载 javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 文件(spring-web META-INF文件夹下), 通过加载该类, 自动扫描所有 WebApplicationInitializer 类型文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
//该方法为 ServletContainerInitializer 的实现方法, 为 servlet3.0 标准
@Override
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
//....省略的代码
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}
需要额外注意的点是: HandlesTypes 这个注解, 它也是 servlet3.0 标准中的, 每个容器都需要实现这个注解的功能, 就是扫描注解内声明的类, 然后传递给onStartup方法
2. 通过 springboot auto config 类(DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration)来启动
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass(DispatcherServlet.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.class)
public class DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Conditional(DefaultDispatcherServletCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebMvcProperties.class)
protected static class DispatcherServletConfiguration {
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet(WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties) {
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet();
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchOptionsRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchOptionsRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchTraceRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchTraceRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(webMvcProperties.isThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound());
dispatcherServlet.setPublishEvents(webMvcProperties.isPublishRequestHandledEvents());
dispatcherServlet.setEnableLoggingRequestDetails(webMvcProperties.isLogRequestDetails());
return dispatcherServlet;
}
}
}
DispatchServlet 如何处理 request 并 response
doService 方法
我们知道这个类继承了HttpServlet, 其为 servlet 标准方法: doService 可以处理所有类型的请求:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
//....省略代码
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
ServletRequestPathUtils.setParsedRequestPath(previousRequestPath, request);
}
}
FlashMap FlashMapManager 这两个类可以为我们处理重定向带来的参数丢失问题, 可以隐式的传递参数, 默认是通过 session 来实现的, 想要得到它也很简单: (FlashMapManager) request.getAttribute(DispatcherServlet.FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE);
doDispatch 方法
通过 doService 方法, 调用了最核心的 doDispatch, 此为核心代码块, 通过几个重要组件来处理 request:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
// handler 处理链, 此对象包含了匹配的 handlerMethod 和 诸多 interceptor
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); // 获取一个异步处理器
try {
ModelAndView mv = null; // 返回的视图信息
Exception dispatchException = null; // 异常信息
try {
// 检查是否是 multipart 类型的请求, 如果是, 使用 multipartResolver, 把流信息处理一下
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
// 获取 handlerChain, 实际上是调用每个 handlerMapping 的 getHandler 方法
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); //noHandlerFound的异常处理
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
// 获取 handlerAdapter, 这个类是最核心的处理类, 由它来实际调用 handlerMethod
// handlerAdapter 中声明了处理 request 所需要的必要组件, 通过一系列适配后, 最终调用 handlerMethod 来返回最终结果
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
// 处理一下 get 请求的缓存策略
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 此处调用拦截器的 preHandler 方法
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
// 处理请求核心方法, 也就是 adapter 的 handle方法, 我们常用的 adapter 就是 requestMappingHandlerAdapter
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { //如果异步处理器启动了, 就不要往下走了
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//调用 interceptor 的 postHandle 方法
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
// 这里把一些 error 也转化为异常, 可以被 exceptionHandler 处理
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
//处理结果
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
//不管有没有异常 都要触发 afterCompletion 方法
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
//不管有没有异常 都要触发 afterCompletion 方法
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { //如果异步处理器启动了, 就不要往下走了
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
//清除 request 的 part 数据 -> Part.delete()
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
WebAsyncManager 解析
这个类是为了处理异步请求的, 耦合了好多的组件 包括不限于: dispatchServlet, requestMappingHandlerMapping, requestMappingHandlerAdapter
该类把 callable 返回值的 handlerMethod 放入了异步队列中去执行, 然后在执行完成后, 使用 response 的 write 写出去, 其中也包括一系列的 interceptor 和 exceptionResolver 的处理
此类需要 servlet3.0 标准的支持, servletRequest 接口增加了startAsync 方法, 用于支持开启异步处理, 此时 response 会一直处于 open 状态, 直到 AsyncContext complete 或 超时
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
//该返回值处理器在 requestMappingHandlerAdapter 中声明, 它在 handle 方法中启动了 WebAsyncManager 的 start 方法
public class CallableMethodReturnValueHandler implements HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler {
@Override
public boolean supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType) {
return Callable.class.isAssignableFrom(returnType.getParameterType());
}
@Override
public void handleReturnValue(@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
if (returnValue == null) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
Callable<?> callable = (Callable<?>) returnValue;
WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(webRequest).startCallableProcessing(callable, mavContainer);
}
}
multipartResolver 处理细节
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
private void parseRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
try {
Collection<Part> parts = request.getParts();
this.multipartParameterNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(parts.size());
MultiValueMap<String, MultipartFile> files = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(parts.size());
for (Part part : parts) {
String headerValue = part.getHeader(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION);
ContentDisposition disposition = ContentDisposition.parse(headerValue);
String filename = disposition.getFilename();
if (filename != null) {
if (filename.startsWith("=?") && filename.endsWith("?=")) {
filename = MimeDelegate.decode(filename);
}
files.add(part.getName(), new StandardMultipartFile(part, filename));
}
else {
this.multipartParameterNames.add(part.getName());
}
}
setMultipartFiles(files);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleParseFailure(ex);
}
}
getHandler 处理细节
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
// ....省略了一些代码
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// Ensure presence of cached lookupPath for interceptors and others
if (!ServletRequestPathUtils.hasCachedPath(request)) {
initLookupPath(request);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
// ....省略了一些代码
return executionChain;
}
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ? (HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(request)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
} else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
handlerAdapter 的 handle 细节
HandlerMapping 指可处理 request 请求的高级抽象, 其实现类有如下:
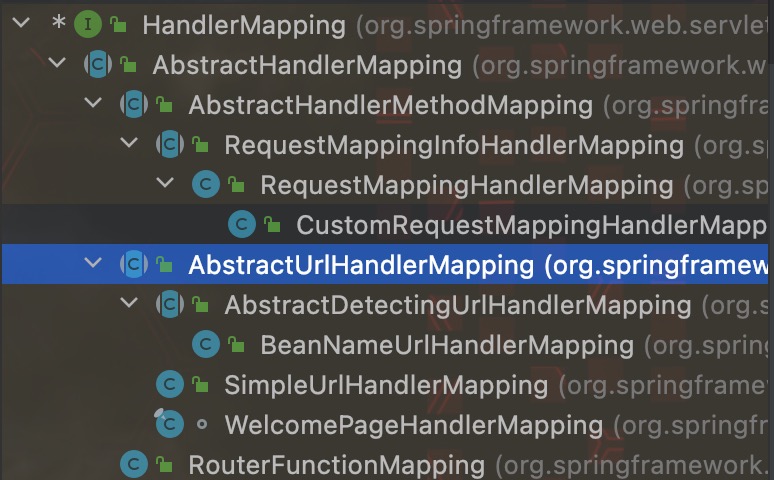
HandlerAdapter 是一种适配器模式, 用来在 request 和 handlerMapping 之间加入一层适配, 使之可以更加完整的去完成 req-resp 的整个流程, 其实现类如下:
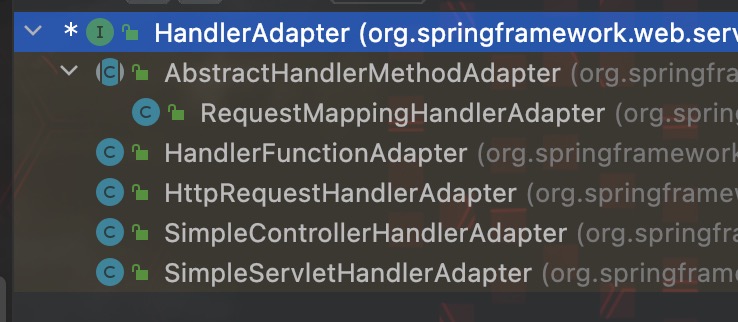
其中常用的 HandlerMapping 除了 springboot 内置的默认 handler, 那只有 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 了
而与之匹配的 adapter 则是 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
HandlerMapping 重要的点:
handlerMethod 是如何生成的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping, 在 bean 实例化之后, 会生成此 HandlerMapping 的所有 handlerMethod 信息
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
还有一个点就是: createRequestMappingInfo 这个方法, 会在调用时, 传入自定义的 condition:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
// 可以传入自定义 condition, 用来干预最终匹配的 handlerMethod, 这里需要去看一下RequestMappingInfo这个类, 需要对其内部原理进行解读
// 通过自定义 condition, 我们可以设计不同版本的 handler URI
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {
RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))
.methods(requestMapping.method())
.params(requestMapping.params())
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name());
if (customCondition != null) {
builder.customCondition(customCondition);
}
return builder.options(this.config).build();
}
HandlerAdapter 重要的点:
其实RequestMappingHandlerAdapter这个类全是知识点, 至少可为我们做编程的口非常多, 这里简单列举一下该类的核心组件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
//自定义参数解析器, 可以通过 WebMvcConfigurer 来配置
@Nullable
private List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> customArgumentResolvers;
//常规参数解析器集合 可以查看: getDefaultArgumentResolvers方法, 熟悉默认的参数解析器
@Nullable
private HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite argumentResolvers;
//自定义绑定器的参数解析器集合 可以查看: getDefaultInitBinderArgumentResolvers方法, 熟悉默认的参数解析器
@Nullable
private HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite initBinderArgumentResolvers;
//自定义返回值 handler, 可以通过 WebMvcConfigurer 来配置
@Nullable
private List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> customReturnValueHandlers;
//返回值 handler 集合, 可以查看: getDefaultReturnValueHandlers方法, 来熟悉默认的返回值 handler
@Nullable
private HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite returnValueHandlers;
//视图解析器 -- 可编程
@Nullable
private List<ModelAndViewResolver> modelAndViewResolvers;
//RESTful 服务中很重要的一个特性: 同一资源可以有多种表述(请求时的 ACCEPT: */*, application/json, text/xml, text/plain),这就是内容协商(ContentNegotiation)处理器
//该处理器可根据客户端支持的内容格式, 返回适当的消息内容(messageConverter)
private ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager = new ContentNegotiationManager();
//消息转换器, 用来处理请求的请求数据以及响应数据的序列化工作 -- 可编程
private List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> messageConverters;
//请求 响应消息的增强类 -- 可编程
private final List<Object> requestResponseBodyAdvice = new ArrayList<>();
//数据绑定处理器
@Nullable
private WebBindingInitializer webBindingInitializer;
adapter 的核心方法是: invokeHandlerMethod, 这个方法最终调用了 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 的 invokeAndHandle方法, 具体请看:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> {
String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn);
return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]";
});
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}
else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
@Nullable
private ModelAndView getModelAndView(ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
ModelFactory modelFactory, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
modelFactory.updateModel(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
return null;
}
ModelMap model = mavContainer.getModel();
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(mavContainer.getViewName(), model, mavContainer.getStatus());
if (!mavContainer.isViewReference()) {
mav.setView((View) mavContainer.getView());
}
if (model instanceof RedirectAttributes) {
Map<String, ?> flashAttributes = ((RedirectAttributes) model).getFlashAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = webRequest.getNativeRequest(HttpServletRequest.class);
if (request != null) {
RequestContextUtils.getOutputFlashMap(request).putAll(flashAttributes);
}
}
return mav;
}
仔细看上述代码, 可对消息做一些增强处理, 而且对 flashMap 做了处理(getModelAndView 方法)
至此全部流程处理完毕